MIDAM MPC5200 DB1: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 326: | Line 326: | ||
* binutils-powerpc-rtems4.9 | * binutils-powerpc-rtems4.9 | ||
* gcc-powerpc-rtems4.9 | * gcc-powerpc-rtems4.9 | ||
* | * rtems4.9-common | ||
* | * rtems4.9-icecube | ||
The configurations used for above binutils, GCC and RTEMS BSP packages build are stored | The configurations used for above binutils, GCC and RTEMS BSP packages build are stored | ||
Revision as of 12:53, 1 January 2010
Description
Two sets of the MIDAM MPC5200 was delivered by the Mikroklima s.r.o. for our purposes. Each set consist of the:
- Shark MPC52000 CPU module (pin compatible with TQ Components TQM5200 module),
- MPC5200 v1.1 2008/02 carrier board.
Set #1 has s/n: 008770 and set #2 has s/n: 008771.
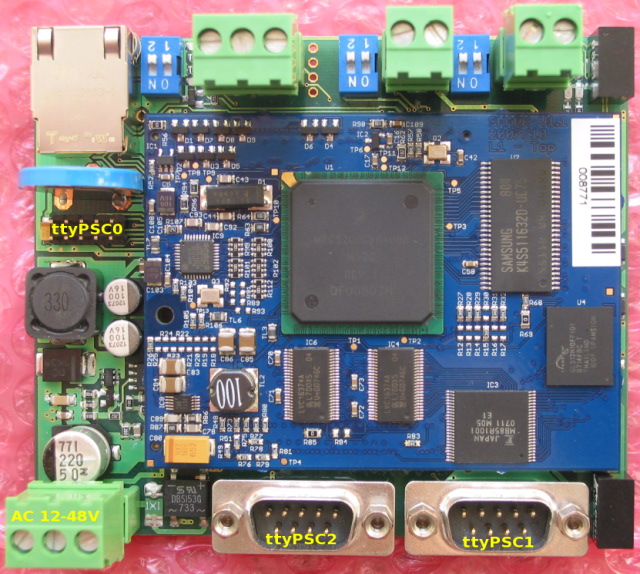
Board overview
Serial line (system console)
- Loader system console is attached to the ttyPSC0 port.
- The ttyPSC0 port is done in the LVTTL 3.3V logic, so appropriate 3.3V to RS-232 converter (e.g. MAX3232) is required for the serial console.
Communication parameters:
- baud rate: 115200 bps
- bits: 8 bit
- stop bits: 1 bit
- Parity: none
- Flow control: none
Module memory map
The MPC5200B is 32 bit CPU, so it has a 32 bit address space. It is able to address up to 4 294 967 295 B (0xFFFFFFFF) - 4096 MB. The Shark module has been equipped with 128 MB DDR RAM and 64 MB NOR flash memory.
- RAM chips: Samsung K4S511632D-UC(L)75, order: 32M x 16
- Address space BASE address is 0x00000000
- RAM is from 0x00000000 to 0x08000000 (128 MB)
Flash memory is being mapped at the and of address space (from 3.9375 GB).
- Flash BASE address is 0xFC000000 (last address is 0xFFFFFFFF)
- Flash memory size is 0x04000000 (64 MB)
There are three MTD partitions in the flash (defined in shark.dts). The flat device tree file syntax uses first address and length of the partition for its definition.
- u-Boot (1 MB) from 0x00000000 to 0x00100000, length 0x00100000
- kernel (3 MB) from 0x00100000 to 0x00400000, length 0x00300000
- file-system (56 MB) from 0x00400000 to 0x04000000, length 0x03C00000
All these addresses are offsets against Flash BASE.
Boot loader
These boards are preinstalled with Das u-Boot boot loader. Behaviour of the u-Boot can be handled by its environment variables. Here are some useful commands:
- printenv [variable] - prints complete environment or only given variable.
- saveenv - commits whole environment in flash memory
For running linux kernel >2.6.25 it's necessary to upgrade u-Boot to newer version, which is able to hand over flat device tree to the kernel. Binary of u-Boot can be downloaded here: u-boot.bin.
U-Boot upgrade howto:
During the upgrade procedure it is necessary to proceed with utmost precaution, because there is no backup image of the u-Boot in the flash for recovery purposes. Fail-flash recovery isn't possible without JTAG interface. So, you have been warned. In future builds of the u-Boot there should be a support for recovery image. Follow this commands to upgrade U-Boot's image in flash memory:
dhcp
tftp 800000 u-boot.bin
protect off fc000000 fc09ffff
erase fc000000 fc09ffff
cp.b 800000 fc000000 ${filesize}
protect on fc000000 fc09ffff
Now reboot and than commit new default environment:
saveenv
How to access U-Boot environment variables from Linux ?
The U-Boot environment variables is possible to read and write trough utilities ... TO DO
Cross-tool chain
Necessary cross-tool chain for PowerPC platform can be build using Crossdev tool. You can install Crossdev on your Gentoo distro very simply:
emerge -av crossdev
Some dependencies may go before. Building of tool chain itself will take some time, so let's go to take some coffee.
crossdev --b 2.18-r3 --k 2.6.23-r3 --g 4.1.2 --without-headers -t powerpc-unknown-linux-gnu
For Debian, you can use a packages prepared by Pavel Píša.
Linux kernel
It is necessary to use patched Linux sources. We maintain them in our Git repository. You can clone it by:
git clone git://rtime.felk.cvut.cz/shark/linux.git
Note: See Linux sources for the description of the repository and patch management techniques we use.
Now let's begin with the kernel configuration. First of all set target platform as Power PC and generate default config for MPC5200 platform.
- export ARCH=powerpc
- make 52xx/midam_defconfig (or use 52xx/ryu_defconfig for RYU board)
- make menuconfig
How to build the Flat Device Tree file
Since kernel version 2.6.25 is description of the platform hardware provided trough the Flat Device Tree. Necessary sources are now part of the kernel sources. Appropriate image could be build with this command:
make ARCH=powerpc shark.dtb DTS_FLAGS="-S65536"
If DTS_FLAGS parameter omitted than following error will occur, because there is not enough space in the file, where the u-Boot can store some additional data about buses timing, etc.:
WARNING: could not create /chosen FDT_ERR_NOSPACE. ERROR: /chosen node create failed - must RESET the board to recover.
Root file system
New root file system has been built for MIDAM MPC5200 board. It's based on:
- Vanilla linux kernel v2.6.26.5
- Busybox v1.12.1
- Dropbear v0.51
- thttpd v2.25b
TO DO - UnionFS for root FS in flash
For long term usage is not really good to repeatedly overwrite block in the NOR flash chip, because memory cells are being punished. So it would be better to use jffs2 root FS only as RO file system and create RW tmpfs of same size. UnionFS than could be used to merge these two file systems and provide one RW file system. Changes in FS as a lock and log files can be made without permanent effect.
SocketCan
make KERNELDIR=/home/marsark/src/linux-2.6.26.5/_build/mpc5200_ryu/ CONFIG_CAN_MPC52XX=m CONFIG_CAN_MSCAN=m
CAN subsystem init script:
modprobe can modprobe mscan-mpc52xx modprobe can-raw
echo 1000000 > /sys/class/net/can0/can_bittiming/bitrate echo 1000000 > /sys/class/net/can1/can_bittiming/bitrate
ifconfig can0 up ifconfig can1 up
Test the setup:
cansend can0 123#4567
GPIO how set pin value
In MPC5200 have two kind of GPIO. The first one have wakeup capability, the second one is standard GPIO pins. Each of this sets have its own register sets, so some PSC ports are splitted in to two parts. See MOC5200B documentation section 7.3.2.1 and 7.3.2.2. The availability GPIO of PSC depends on GPS Port Configuration Register settings. For RYU boards is available all GPIO in PSC3 port (HW notation).
TODO: kernel still fails to initialise GPIO drivers on our boards !!!
cat /sys/class/gpio/gpiochip248/label //todo
Setting GPIO with wakeup capability
GPIO with wakeup using
/sys/class/gpio/gpiochip248/
Pin notation:
0 -> GPIO_WKUP_7 1 -> GPIO_WKUP_6 2 -> PSC6_1 3 -> PSC6_0 4 -> ETH_17 5 -> PSC3_9 6 -> PSC2_4 7 -> PSC1_4
Final value is 248 + requested pin (example for PSC2_4 248+6 => 254)
Enable PIN for GPIO:
echo 254 >/sys/class/gpio/export
Set GPIO as output or input
echo out >/sys/class/gpio/gpio254/direction echo in >/sys/class/gpio/gpio254/direction
Set GPIO to 0 or 1 if configured as output pin
echo 0 >/sys/class/gpio/gpio254/value echo 1 >/sys/class/gpio/gpio254/value
Setting standard GPIO not tested
Standard GPIO using
/sys/class/gpio/gpiochip216/
Pin notation:
0..1 > reserved 2..3 > IRDA 4..7 > ETHR 8..11 > reserved 12..15 > USB 16..17 > reserved 18..23 > PSC3 24..27 > PSC2 28..31 > PSC1
Final value is 216 + requested pin (example for PSC3_3 216+20 => 236)
Enable PIN for GPIO:
echo 236 >/sys/class/gpio/export
Set GPIO as output or input
echo out >/sys/class/gpio/gpio236/direction echo in >/sys/class/gpio/gpio236/direction
Set GPIO to 0 or 1 if configured as output pin
echo 0 >/sys/class/gpio/gpio236/value echo 1 >/sys/class/gpio/gpio236/value
RS485/RS422 selection on PSC1
In MPC5200 or schematic it is PSC2. In linux is PSC numbered from 0 so it is PSC1.
Pin configuration:
echo 254 >/sys/class/gpio/export echo out >/sys/class/gpio/gpio254/direction
Run for RS485:
echo 1 >/sys/class/gpio/gpio254/value
Run for RS422:
echo 0 >/sys/class/gpio/gpio254/value
Linux boot possibilities
PIN configuration
Bootloader is responsible for pin configuration. This is done by writing to GPS Port Configuration Register. The value written there is set by:
set psc_cfg 91551044
GPS Port Configuration Register values for our boards:
- original Midam board: 0x90552444
- RYU_EDU_midam v1.B: 0x91551044
Kernel and root filesystem from flash
This is the default boot command. If you want to quickly switch several boot combinations, you can store these commands to a variable and use run command to boot linux from flash quickly.
set bootcmd_linux 'set bootargs ${linux_console} ${bootargs_flash}; mw f0000b00 ${psc_cfg}; bootm fc120000 - fc100000'
set bootcmd 'run bootcmd_linux'
Kernel from flash and root filesystem over NFS
bootcmd_nfsroot=set bootargs ${linux_console} ${bootargs_nfs}; dhcp; mw f0000b00 ${psc_cfg}; bootm fc120000 - fc100000;
bootargs_nfs=root=/dev/nfs nfsroot=/midam rw ip=dhcp
run bootcmd_nfsroot
Kernel from TFTP and root filesystem over NFS
set serverip 147.32.86.30
set nfspath "/home/wsh/ppc/MPC5200/root-shark"
set imagefile ryu/uImage
set devicetreefile ryu/shark-ryu.dtb
set bootcmd_tftpnfs 'dhcp; tftp 800000 ${imagefile}; tftp 7f0000 ${devicetreefile}; set bootargs ${linux_console} root=/dev/nfs nfsroot=${serverip}:${nfspath} rw ip=dhcp; mw f0000b00 ${psc_cfg}; bootm 800000 - 7f0000'
run bootcmd_tftpnfs
Updating kernel image in flash memory
set serverip 10.1.1.3 set imagefile ryu/uImage set devicetreefile ryu/shark-ryu.dtb run update_kernel
It is supposed that update_kernel is set to the following value
set update_kernel 'dhcp; tftp 800000 ${imagefile}; erase fc100000 fc3fffff; cp.b 800000 fc120000 ${filesize}; tftp 800000 ${devicetreefile}; cp.b 800000 fc100000 ${filesize};'
Updating root filesystem image in flash memory
From Linux with NFS root
Erase flash in U-Boot:
erase fc400000 ffffffff
Boot Linux with NFS root and run:
mount -t jffs2 /dev/mtdblock2 /mnt cd / cp -a `ls | grep -v '\(mnt\|proc\|sys\|tmp\)'` /mnt cd /mnt; mkdir mnt proc sys tmp
From U-Boot
FIXME: This section needs some tuning. It works, but there are some problems.
Note: There seem to be no problems, if you use correct erase block size, when creating the FS image, i.e. use -e 0x20000 instead of -e 0x10000 (Martin Zidek)
Prepare filesystem image in a development machine and create the filesystem image:
cd shark-root mkfs.jffs2 -o ../shark-jffs2.img -b -e 0x10000 cp ../shark-jffs2.img /var/lib/tftpboot/ryu/
Then flash the image using the following uboot commands:
set fs_image ryu/shark-jffs2.img
set update_filesystem 'dhcp; tftp 800000 ${fs_image}; erase fc400000 ffffffff; cp.b 800000 fc400000 ${filesize}'
run update_filesystem
Running RT kernel
cyclictest -p 80 -t5 -n 0.93 0.68 0.28 1/51 562
T: 0 ( 544) P:80 I:1000 C: 354314 Min: 16 Act: 76 Avg: 69 Max: 190 T: 1 ( 545) P:79 I:1500 C: 236209 Min: 17 Act: 35 Avg: 53 Max: 131 T: 2 ( 546) P:78 I:2000 C: 177157 Min: 21 Act: 46 Avg: 56 Max: 123 T: 3 ( 547) P:77 I:2500 C: 141726 Min: 21 Act: 41 Avg: 53 Max: 155 T: 4 ( 548) P:76 I:3000 C: 118105 Min: 23 Act: 30 Avg: 56 Max: 126
Booting VxWorks
set ethaddr 00:04:9f:00:27:xx
set psc_cfg 91551044
set bootcmd_vxworks 'set serverip 147.32.87.33; dhcp; mw f0000b00 ${psc_cfg}; tftp 0x100000 vxworks/vxWorks-midam.bin; go 0x100000'
set bootcmd 'run bootcmd_vxworks'
saveenv
Older tests:
dhcp; set serverip 147.32.86.187; set bootfile vxWorks.bin; tftp 0x00100000; go 0x00100000
Compiling VxWorks
It is assumed that VxWorks in installed under /opt/WindRiver
/opt/WindRiver/wrenv.sh -p vxworks-6.6 cd <bsp_project> make ... TODO ...
RTEMS Support
MIDAM MPC5200 board is compatible with RTEMS IceCube BSP.
The PowerPC cross-compiler tool-chain for RTEMS-4.9 branch for Debian Intel 32 and 64-bit hosts can be installed from Rtime local DEB repository [1].
- Add APT source:
echo deb ftp://rtime.felk.cvut.cz/debian unstable main >/etc/apt/sources.list.d/rtime-debs.list
- Update list of available packages
apt-get update
Next packages can be installed from cross-dev section (e.g. using apt-get, aptitude or synaptic)
- binutils-powerpc-rtems4.9
- gcc-powerpc-rtems4.9
- rtems4.9-common
- rtems4.9-icecube
The configurations used for above binutils, GCC and RTEMS BSP packages build are stored in local RTEMS development GIT repository in a build directory for PowerPC architecture.
The short cross-tools build recipe:
git clone git://rtime.felk.cvut.cz/rtems-devel.git cd rtems-devel mkdir src cd src tar -xjf path-to/gcc-4.3.4.tar.bz2 ln -s gcc-4.3.4 gcc tar -xjf path-to/binutils-2.20 ln -s binutils-2.20 binutils tar -xzf path-to/newlib-1.16.0.tar.gz ln -s newlib-1.16.0 newlib cd gcc ln -s ../newlib/newlib . ln -s ../../gcc-patches/4.3.4 patches quilt push -a cd ../newlib ln -s ../../newlib-patches/newlib-1.16.0 patches quilt push -a cd ../.. ln -s src/gcc src/binutils src/rtems . ( cd rtems-build/powerpc-rtems/binutils && ./binutils-powerpc-rtems.cfg && make && make install ) ( cd rtems-build/powerpc-rtems/gcc && ./gcc-powerpc-rtems.cfg && make && make install ) ( cd rtems-build/powerpc-rtems/rtems-icecube && ./rtems-mpc5200-sys.cfg && make && make install )
Applications can be easily build by starting from RTEMS application template based on OMK rules:
cd rtems-omk-template echo "RTEMS_MAKEFILE_PATH=/opt/rtems4.9/powerpc-rtems4.9/icecube" >config.target make default-config all
Compiled application ELF images are located in _compiled/icecube/bin directory. The ELF file needs to be be converted into U-boot image to be transferred and started on target board
powerpc-rtems4.9-objcopy -R -S -O binary appfoo appfoo.bin cat appfoo.bin | gzip -9 >appfoo.gz mkimage -A ppc -O rtems -T kernel -a 0x00010000 -e 0x00010000 -n RTEMS -d appfoo.gz appfoo.img
The image tranfer and boot sequence can be initiated from target board U-boot prompt
mw f0000b00 ${psc_cfg}
dhcp
#set serverip 192.168.202.251
tftp 1000000 appfoo.img
bootm
The script rtems-mpc5200-mkimg to pack ELF file to U-boot image is part of development repository as well.