Temperature reading application: Difference between revisions
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
<br>2. The following escaped are used for maintaing the framing byte protocol | <br>2. The following escaped are used for maintaing the framing byte protocol | ||
0x7E -> 0x7D 0x5E | 0x7E -> 0x7D 0x5E | ||
0x7D -> 0x7D 0x5D | |||
=== Example === | === Example === | ||
Latest revision as of 15:17, 21 April 2007
This Nesc/TinyOS application is for measuring the temperature with maximum of two sensors. One acts like a Base Station and has to be connected with the USB connection to the computer. The second acts like a Remote Station and transmitts its temperature reading via the radio to the Base Station. At the final stage, the Base Station transmitts the complete data, both temperature readings, to the computer every second. Please note that the application described here can be used without any Remote Station.
In this document it is described how to install the Nesc/TinyOS application TRead and how to retreive and interpret the data.
It is assumed that the installation of TinyOS 1.x and Nesc is installed with the nessecary components.
Installation of the application
Extract the TRead.zip application in the folder xxx/tinyos-1.x/apps/. Then in the folder xxx/tinyos-1.x/apps, install the application by following line:
(For Tmote Sky connected to USB port 0)
make telosb && make telosb install.$2 bsl,/dev/ttyUSB0
NOTE!
In the file TReadM.nc, at the top, there is a preprocessor definition #define BASE_STATION.
When installing for the Remote station, comment this line and install as described above. For Base Station, leave it as it is.
Retrieving the data
Extract the TReadSerial.zip file. Here, you will find a C++ class called CSerialCom that can be used for retreiving the data.
API:
Opens the connection to a serial device
with i.e "/dev/USB0" (Linux)
int openDevice(const char* pDevice)
Closes the connection to the serial device
void closeDevice(void)
Settings for the serial device
IN: Only type available: TYPE_TMOTE_SKY
void setOptions(int type)
Retreives the data from the serial port if any available. Max waiting
time for the data retreival is 6s. Where after the return value will be 0.
IN: pData: where the data should be stored. allocated by the caller
Return: Nr of bytes allocated in the pData buffer.
int getData(char* & pData)
Sends the to the serial device NOTE! Doesn't work!
IN: pData: buffer to transmitt
length: number of bytes to send from the buffer
int sendData(uint8_t* pData, int length);
Interpretting the data
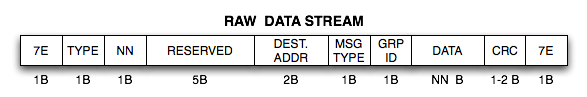
The data is retrived in so called raw format as following:
7E: The leading and trailing framing byte 0x7E can be ignored.
TYPE: In this application, 0x42 Which means no acknowledge is required.
NN: Number of bytes of data that is sent in this packet
RESERVED: TMote reservation
DEST. ADDR: Packet destination. In this application: 0xFF 0xFF
MSG TYPE: Not used in this application. Always: 0x01
GRP ID: Group ID. Default set to 0x7D
DATA: NN bytes of data sent. Explained further down
CRC: Checksum (ignored)
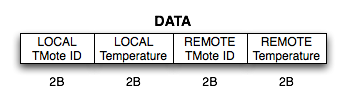
DATA
The encapsulated data is in the following format:
LOCAL = Base Station
REMOTE = Remote Station
NOTE!
1. The raw stream is in Little Endian format
2. The following escaped are used for maintaing the framing byte protocol
0x7E -> 0x7D 0x5E 0x7D -> 0x7D 0x5D
Example
The data will be retreived as following (HEX VALUES)
7E 42 08 00 00 00 00 00 7D 5E 00 01 7D 5D XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX RR (RR) 7E
After removing the framing bytes and the escape code sequences, the ACTUAL packet is:
42 08 00 00 00 00 00 7E 00 01 7D XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX RR (RR)
TYPE is 42 (NO_ACK). Data length is 8 bytes in the data region.
Additional
The temperature can be calculated with the following C# code. However, it's not tested:
Calculating Temperature in Engineering Units
/// <summary>
/// Calculates the temperature, in degrees Celsius of the:
///
/// Panasonic ERT-J1VR103J Thermistor
///
/// The formula in the MTS Series User Manual is:
/// 1/T(K) = a + b × ln(Rthr) + c × [ln(Rthr)]^3
///
/// where:
/// Rthr = R1(ADC_FS-ADC)/ADC
/// a = 0.00130705
/// b = 0.000214381
/// c = 0.000000093
/// R1 = 10 kOhm
/// ADC_FS = 1023
/// ADC = output value from mote’s ADC measurement.
///
/// Note that an adjusted temp (adjTemp) is used because the
/// actual temp reading is a 10 bit value that has been compressed
/// into a single byte. As such it must be shifted left 2 bit places.
///
/// The value for _temp is the raw sensor reading from the SurgeMsg.
///
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Temperature in Degrees Celsius as a float.</returns>
float CalculateTempC()
{
int adjTemp = _temp << 2;
// prevent divide by zero.
if(adjTemp == 0)
return 0F;
float temperature, a, b, c, Rthr;
a = 0.001307050F;
b = 0.000214381F;
c = 0.000000093F;
Rthr = 10000 * (1023 - adjTemp) / adjTemp;
temperature = 1 / (float)(a + b * Math.Log(Rthr) + c *
Math.Pow(Math.Log(Rthr),3));
temperature -= 273.15F; // Convert from Kelvin to Celcius
}